
Overview
In the rapidly evolving world of agriculture, technology is playing an essential role in helping farmers achieve greater efficiency and higher yields. Precision farming has emerged as a solution for the challenges faced in modern agriculture, focusing on using data-driven insights to optimise farming operations.
Drones, such as the DJI Mavic 3 Multispectral (M3M), are now an integral part of precision agriculture, providing real-time, detailed aerial data that can be used to make more informed decisions. This blog explores how drones are revolutionising crop spraying, health inspections, and harvest planning, with a fictional farm case study.

Challanges
In our fictional case study, GreenFields Farm, a 500-acre farm growing wheat and corn, faced several challenges common to many large-scale operations. The farmers were dealing with over-application of fertilisers and pesticides, causing environmental harm and increased costs.
Additionally, they lacked timely insights into crop health, resulting in reduced yields and poor crop management. Finally, determining the optimal harvest time was a constant struggle, often leading to underperformance in return on investment (ROI) due to suboptimal crop conditions during harvesting.
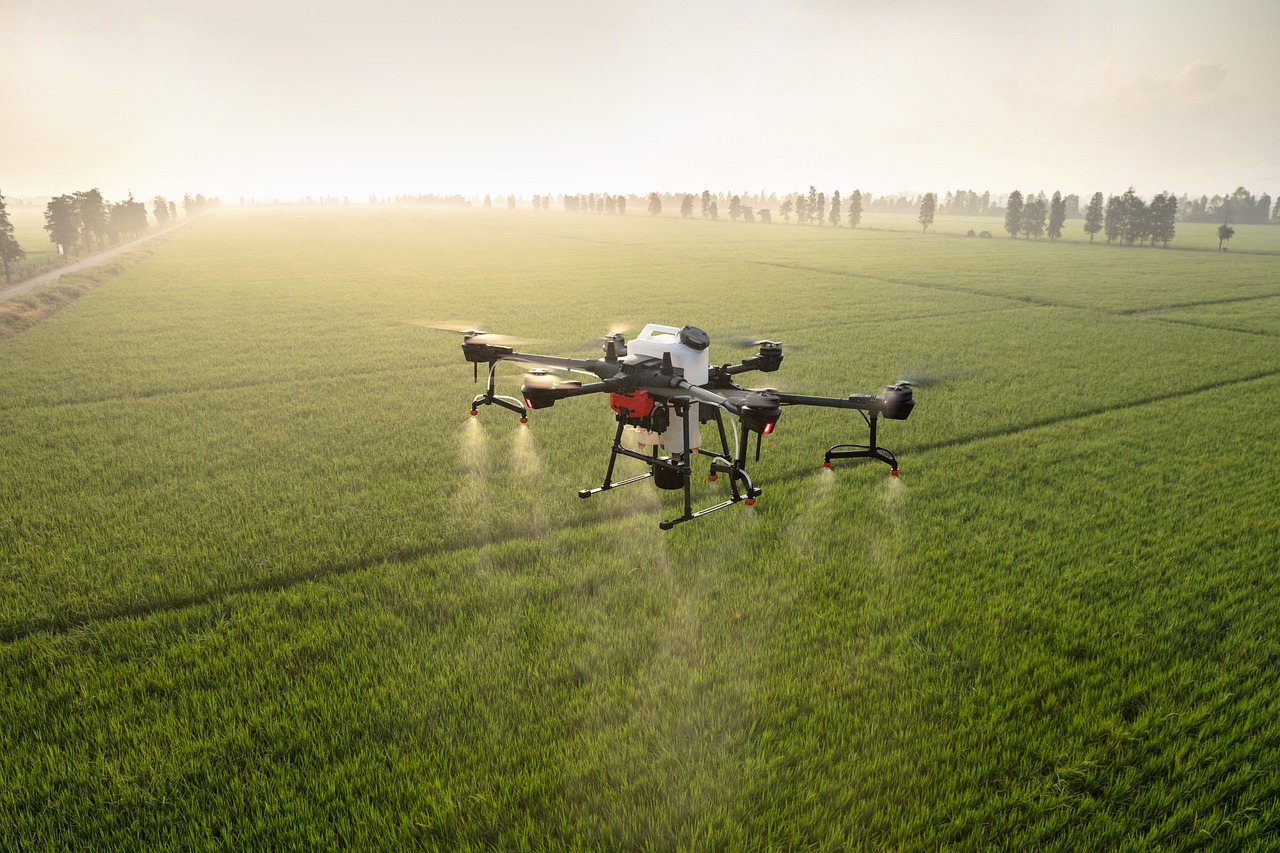

Implementation of Drone Technology
To address these challenges, GreenFields Farm implemented the DJI Mavic 3 Multispectral (M3M), a drone equipped with advanced imaging sensors capable of capturing high-resolution data. The drone was used to perform multiple tasks:
- Precision Spraying Coordination: The DJI M3M communicated directly with GPS-enabled tractors, identifying specific areas of the farm that needed targeted applications of fertilisers and pesticides. Instead of broad spraying, the drone’s sensors identified problem areas requiring attention, leading to significant reductions in chemical use.
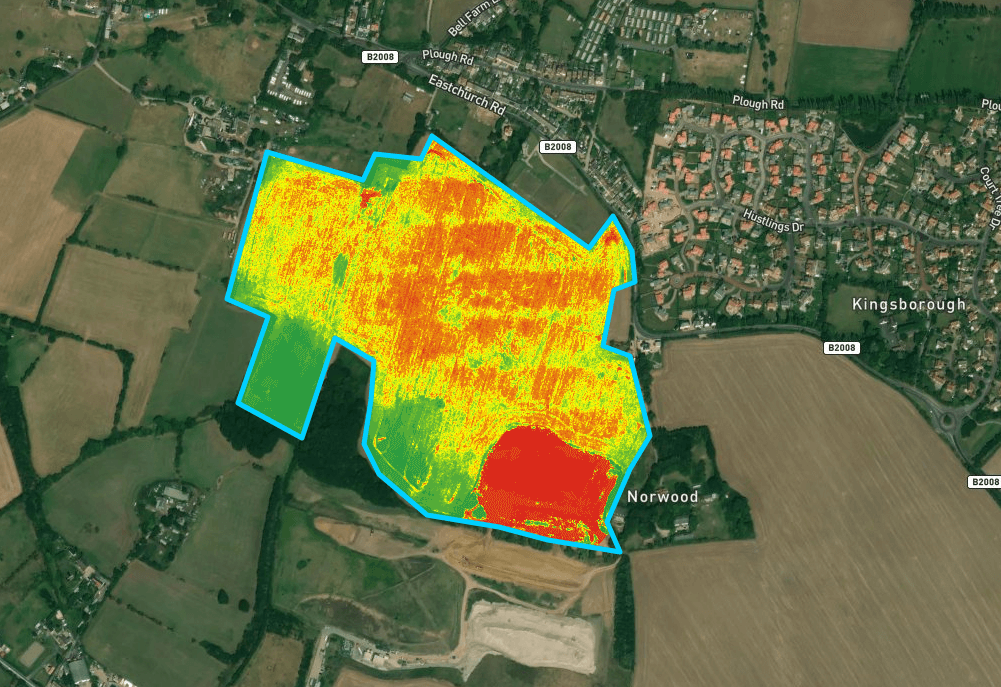
- Crop Health Inspections: Utilizing its multispectral sensors, the DJI M3M performed regular crop health inspections, generating real-time NDVI (Normalised Difference Vegetation Index) maps. These maps provided critical information on plant health, allowing the farm to adjust irrigation, nutrients, and pest control for each crop zone.
- Harvest Optimisation: The drone also gathered data on plant maturity and predicted the ideal harvesting time. Using this data, GreenFields Farm was able to schedule harvesting operations when the crops were at peak ripeness, leading to an increased yield and improved quality of the produce.

Advantages of Drones in this Case Study
The introduction of the DJI M3M drone into GreenFields Farm’s operations resulted in several key advantages:
- Reduced Chemical Use: Targeted spraying, informed by drone data, led to a 30% reduction in fertilisers and pesticides, lowering costs and minimising environmental impact.
- Improved Crop Health: Regular crop inspections and timely interventions based on drone insights increased yields by 15%, as problems such as nutrient deficiencies and pest infestations were addressed earlier.
- Optimized Harvest Timing: With better data on crop maturity, the farm was able to plan harvests more effectively, resulting in a 10% increase in crop yield and quality, maximising the ROI.
- Increased Efficiency: The drone reduced the need for manual inspections, saving time and labor costs while ensuring more consistent monitoring of crop health across the entire farm.
Software
GreenFields Farm utilised DJI’s proprietary software, DJI Pilot 2, for flight planning and data collection. Pilot 2s robust mapping capabilities allowed the farm to ensure all aspects were covered and the correct information automaticaly calculated to ensure full data coverage.
In addition, a third-party precision farming software, was integrated for advanced crop analytics. This enabled GreenFields Farm to generate prescription maps that were fed into the GPS-controlled tractors, which automated the precision spraying process based on real-time drone data.

Data Processing
The data collected by the DJI M3M drone went through several stages of processing.
- Aerial Imaging: The drone’s multispectral sensors captured images in different wavelengths, allowing detailed analysis of plant health that goes beyond the visible spectrum.
- NDVI Analysis: These images were processed to create NDVI maps, which helped identify areas where crops were stressed or underperforming. High NDVI values indicated healthy vegetation, while lower values suggested issues like nutrient deficiency or pest infestations.
- Prescription Maps: Based on the processed data, the farm management team generated prescription maps. These maps pinpointed specific areas of the farm that required varying levels of fertilizers, water, or pesticides, making farming operations more targeted and efficient.
- Cloud Storage: All drone data was stored in the cloud, allowing the farm team to access and analyze historical data to identify trends, further improving decision-making for the next growing season.
