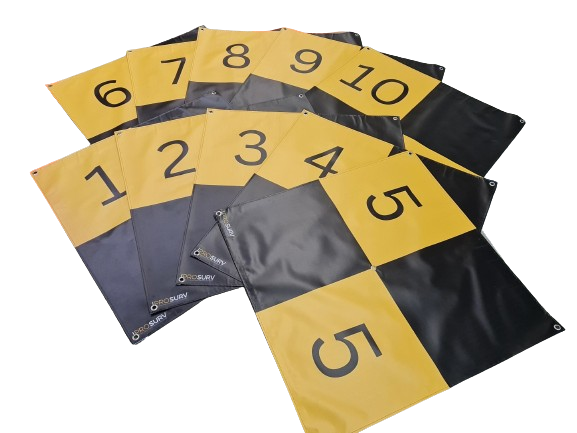
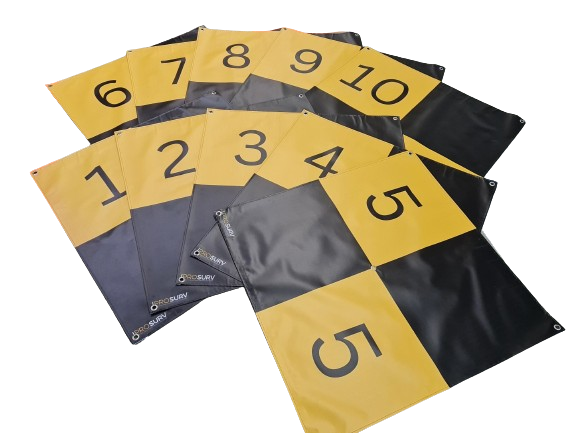
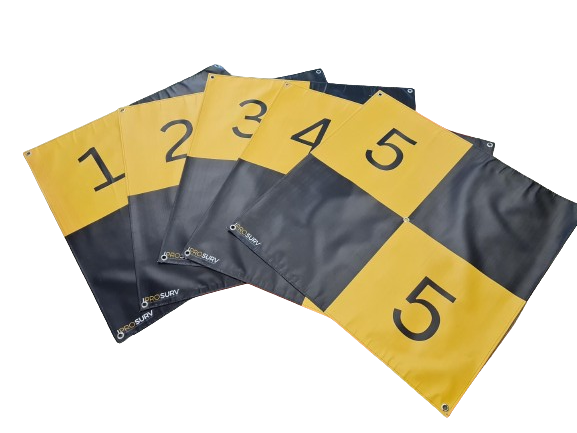
Drone Ground Control Points (GCPs) are marked points on the ground with known geographic coordinates.
They serve as reference points for aerial surveying and mapping using drones or other aerial platforms. GCPs play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy of the data collected during aerial surveys, particularly in photogrammetry, where multiple images are stitched together to create detailed maps or 3D models.
Our ground control points are made of waterproof 440gsm material which is ideal for any site and can be wiped down after use in bad weather or in dirty environments.
Our GCP’s?
- Can be custom made in your own colours but we do have a range a pre-designed products.
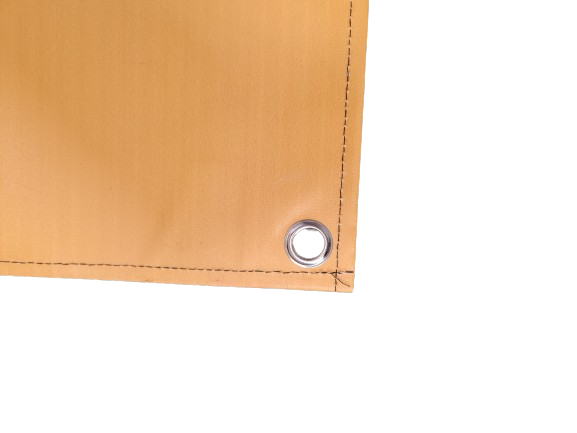
- Banners have re-inforced stitching around the outside and also have stainless steel eyelets at each corner for pegging down.
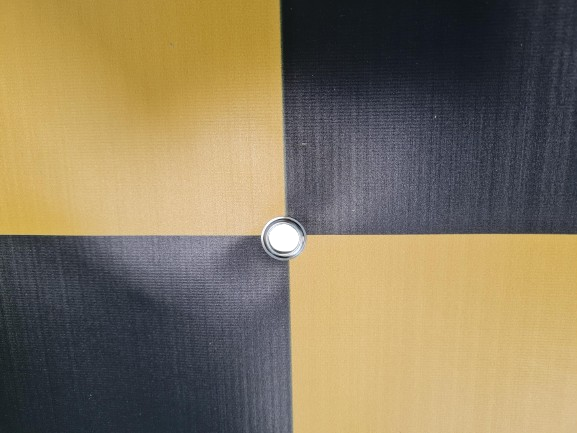
- There is a centre hole to accomodate a gps rover.
- Can also be white labeled with your own branding.
- Can be ordered in multiples of 5 (5,10,15,20) etc.
- Discounts can be applied for multiple orders.
- Large format 90CM x 90CM so panels are easily visable.
- Come in a range of colours.
- Reseller option with discounted supply (email us for more information).